Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis
- Manuel Lim, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):102-112. Published online February 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.01.31
- 407 Views
- 38 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
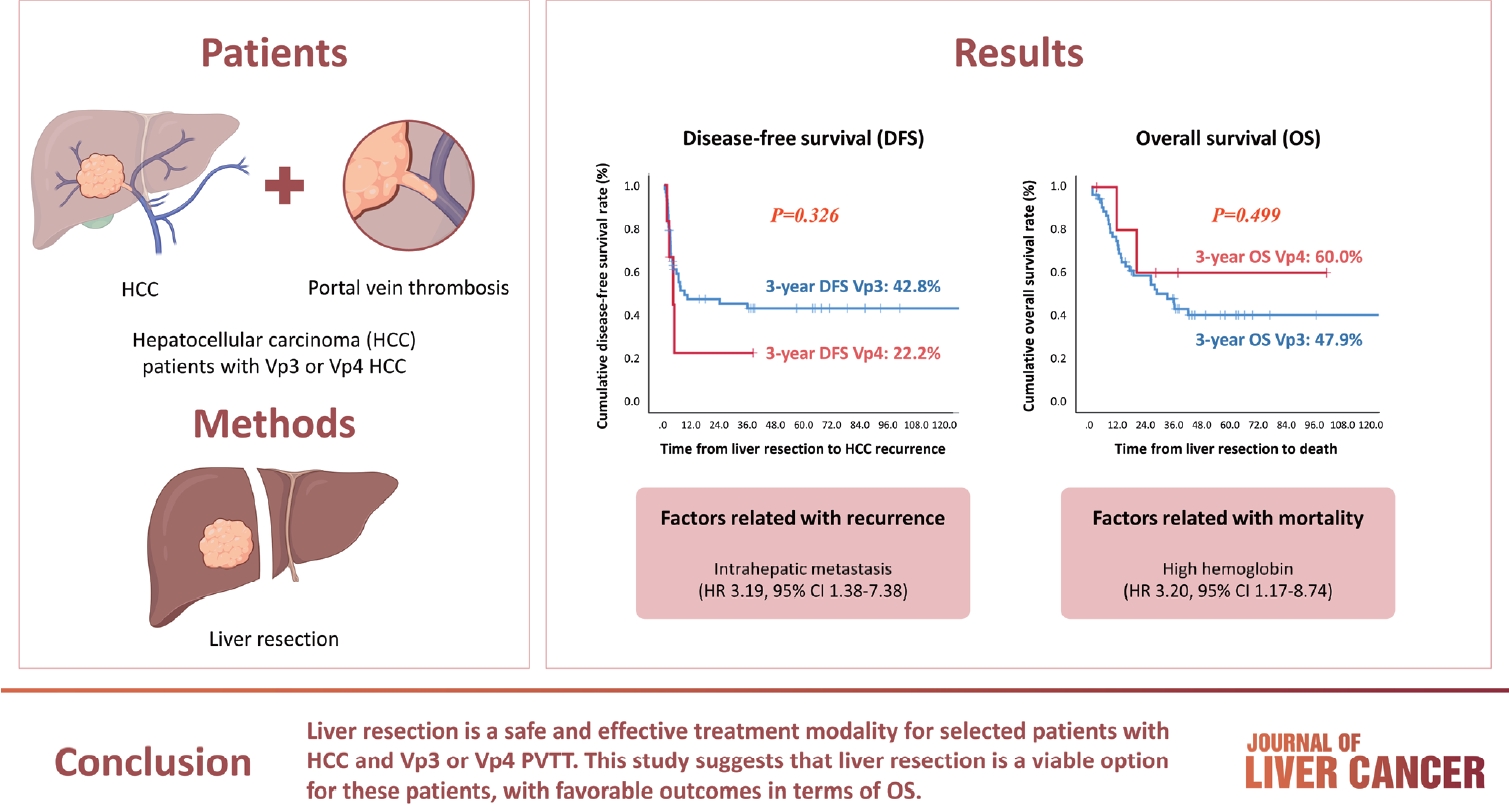
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumor thrombi located in the first branch of the portal vein (Vp3) or in the main portal trunk (Vp4) are associated with poor prognosis. This study aimed to investigate the clinicopathological characteristics and risk factors for HCC recurrence and mortality following liver resection (LR) in patients with Vp3 or Vp4 HCC.
Methods
The study included 64 patients who underwent LR for HCC with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT).
Results
Fifty-eight patients (90.6%) had Vp3 PVTT, whereas the remaining six patients exhibited Vp4 PVTT. The median tumor size measured 8 cm, with approximately 36% of patients presented with multiple tumors. Fifty-four patients (84.4%) underwent open LR, whereas 10 patients underwent laparoscopic LR. In the Vp4 cases, combined LR and tumor thrombectomy were performed. The 3-year cumulative disease-free survival rate was 42.8% for the Vp3 group and 22.2% for the Vp4 group. The overall survival (OS) rate at 3 years was 47.9% for the Vp3 group and 60.0% for the Vp4 group. Intrahepatic metastasis has been identified as an important contributor to HCC recurrence. High hemoglobin levels are associated with high mortality.
Conclusion
LR is a safe and effective treatment modality for selected patients with Vp3 or Vp4 HCC PVTT. This suggests that LR is a viable option for these patients, with favorable outcomes in terms of OS.

- Indications for open hepatectomy in the era of laparoscopic liver resection: a high volume single institutional study
- Sung Jun Jo, Jinsoo Rhu, Jong Man Kim, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):146-157. Published online September 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.08.22
- 2,309 Views
- 60 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Since the introduction of laparoscopy for liver resection in the 1990s, the performance of laparoscopic liver resection (LLR) has been steadily increasing. However, there is currently no data on the extent to which laparoscopy is used for liver resection. Herein, we investigated the extent to which laparoscopy is performed in liver resection and sought to determine whether surgeons prefer laparoscopy or laparotomy in the posterosuperior (PS) segment.
Methods
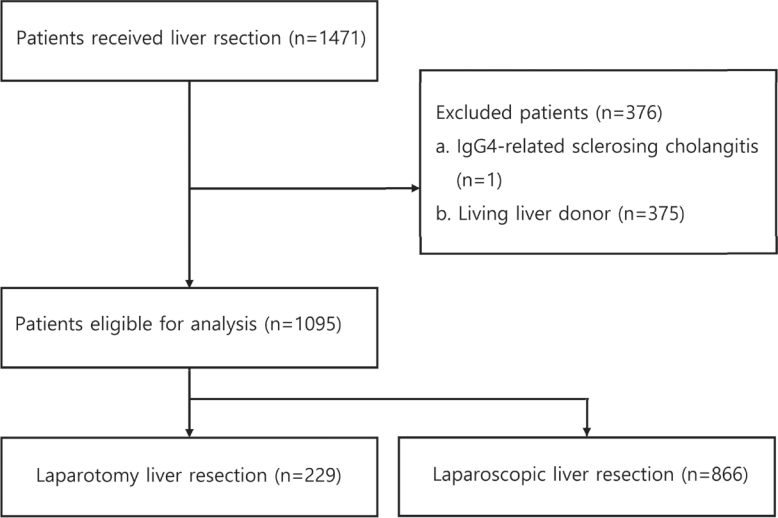
For this retrospective observational study, we enrolled patients who had undergone liver resection at the Samsung Medical Center between January 2020 and December 2021. The proportion of LLR in liver resection was calculated, and the incidence and causes of open conversion were investigated.
Results
A total of 1,095 patients were included in this study. LLR accounted for 79% of the total liver resections. The percentage of previous hepatectomy (16.2% vs. 5.9%, P<0.001) and maximum tumor size (median 4.8 vs. 2.8, P<0.001) were higher in the open liver resection (OLR) group. Subgroup analysis revealed that tumor size (median 6.3 vs. 2.9, P<0.001) and surgical extent (P<0.001) in the OLR group were larger than those in the LLR group. The most common cause of open conversion (OC) was adhesion (57%), and all OC patients had tumors in the PS.
Conclusions
We investigated the recent preference of practical surgeons in liver resection, and found that surgeons preferred OLR to LLR when treating a large tumor located in the PS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sujin Koo, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Dong Ah Park
Current Oncology.2024; 31(1): 324. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of blood transfusion rates during liver resection by country
Seonju Kim, Yun Kyung Jung, Kyeong Geun Lee, Kyeong Sik Kim, Hanjun Kim, Dongho Choi, Sumi Lee, Boyoung Park
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2023; 105(6): 404. CrossRef
- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

Case Report
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Arising from Hepatocellular Adenoma in an Elderly Male Patient
- Manuel Lim, Jong Man Kim, Ji Eun Kwon, Eun Sung Jeong, Jaehun Yang, Okjoo Lee, Kyeong Deok Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):87-91. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.87
- 4,009 Views
- 95 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
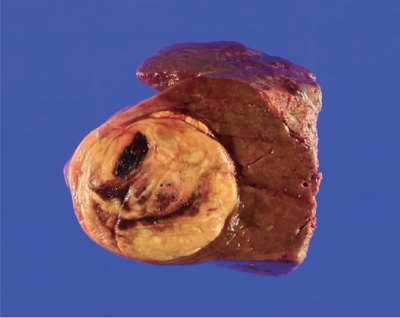
PDF - Hepatocellular adenoma is a benign tumor of the liver occurring predominantly in young women taking oral contraceptives. The malignant transformation of hepatocellular adenoma into hepatocellular carcinoma has rarely been reported. Herein, we report the case of an elderly male patient with hepatocellular carcinoma that developed from hepatocellular adenoma. The patient’s high risk for surgery and conflicting biopsy and imaging results made it difficult to determine the treatment direction. Eventually, the mass was completely removed by laparoscopic left hemi-hepatectomy without complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sujin Koo, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Dong Ah Park
Current Oncology.2024; 31(1): 324. CrossRef
- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

Original Article
- Cirrhosis in Surgically Resected Hepatitis C-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Hepatitis B Endemic Area
- Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Jae-Won Joh, Seung Woon Paik, Byung Chul Yoo, Cheol Keun Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):108-114. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.108
- 841 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Cirrhosis has generally been considered a prerequisite for hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected livers to develop hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but HCCs that arise in absence of cirrhosis has been reported. We assessed the prevalence and significance of cirrhosis in HCV-related HCC patients who underwent surgical resection.
Methods
A total of 78 HCC patients (65 male [83.3%]; mean age, 64.2 ± 8.6 years) were evaluated for the presence of cirrhosis. Cirrhosis was assessed based on histology, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI) as well as clinical criteria, such as ascites, varices, thrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, and radiographic configuration of cirrhosis.
Results
Based on histology, cirrhosis, septal fibrosis, periportal fibrosis and no fibrosis was noticed in 33.3%, 60.3%, 5.1% and 1.3% of patients, respectively. The clinical criteria of cirrhosis were present in 76.9% of patients. APRI > 1.0 was seen in 47.4% of patients. There was no evidence of cirrhosis in 18 patients (23.1%), either by histology or clinically. Cirrhosis by histology was an independent factor for overall survival [hazard ratio: 3.87 (95% CI: 1.24 – 12.00), P=0.019].
Conclusions
Quite proportion of HCC patients had no evidence of cirrhosis, either by histology or clinically. Careful follow-up for HCC may be necessary even for non-cirrhotic HCVinfected Korean patients. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:108-114)


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter